 | ||
| || home ||| units ||||| help | ||
| All Units | > | Unit 1 - Sound | > | Investigation 2 - Making and Hearing Sounds | > | Analysis |
Analysis
-
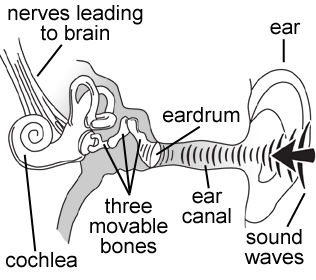
Your eardrum is a piece of skin just like a stretched balloon. It vibrates when sounds reach your ear. Bones that touch the eardrum carry the vibrations to your inner ear, where they are detected and translated into signals to the brain. Here is a diagram of the ear. Can you explain why sounds aren't as loud when you cover your ear?

-
What is the loudest sound you ever heard? Did it hurt your ears?

-
What is the quietest sound you are able to hear?

-
Cup your ears with your hands and see if you can hear quiet sounds better. Based on what you observe, what is the purpose of your outer ear?


-
A microphone is very much like an ear. Sounds make a surface vibrate, which moves a magnetic coil that produces electrical signals. Here is a diagram.
-
Here is a diagram of a loudspeaker. It's like an ear working backwards. It changes electrical signals into sound vibrations. How does it look like an eardrum? How does it work like an ear in reverse?


-
We don't 'pluck' our vocal cords. What do you think makes them vibrate?

-
Here are diagrams of several musical instruments. Identify what vibrates to make the sound. How does the player make it vibrate? How does the player control the pitch and the loudness of the sound?




Instrument What vibrates Change loudness by: Change pitch by: Violin 


Saxophone 


Trombone 


Timpani 



 |  |  |
Copyright 2005 The Concord Consortium, All rights reserved.